Describe the Basic Process of Dna Replication in a Cell
When a cell divides it must first duplicate its genome so that each daughter cell winds up. This area will be the template for replication to begin.

What Are The Steps Of Dna Replication
For gamete formation meiosis occurs.

. This process allows the DNA to be compacted into the small space inside a bacteria. It is also necessary for evolution and immune system response. DNA replication is the biological process in which two identical copies of DNA are produced from one original DNA molecule.
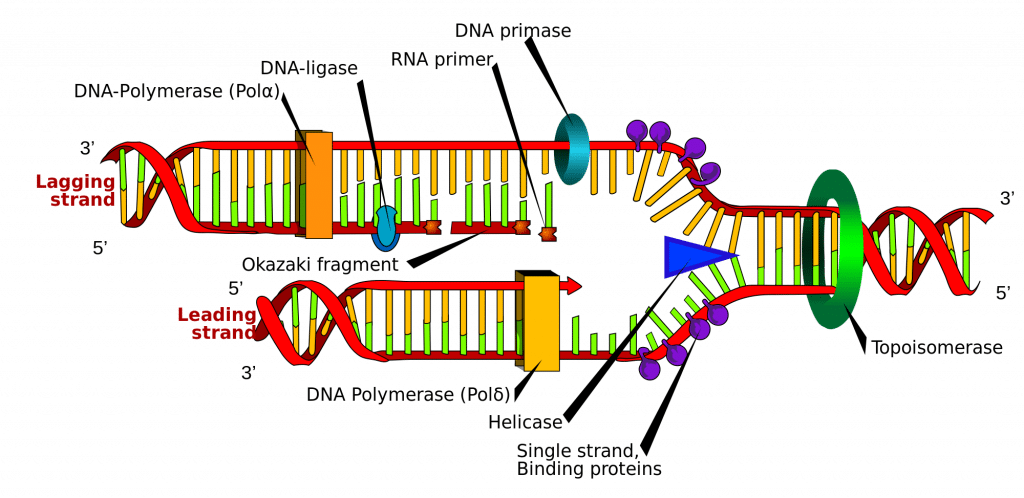
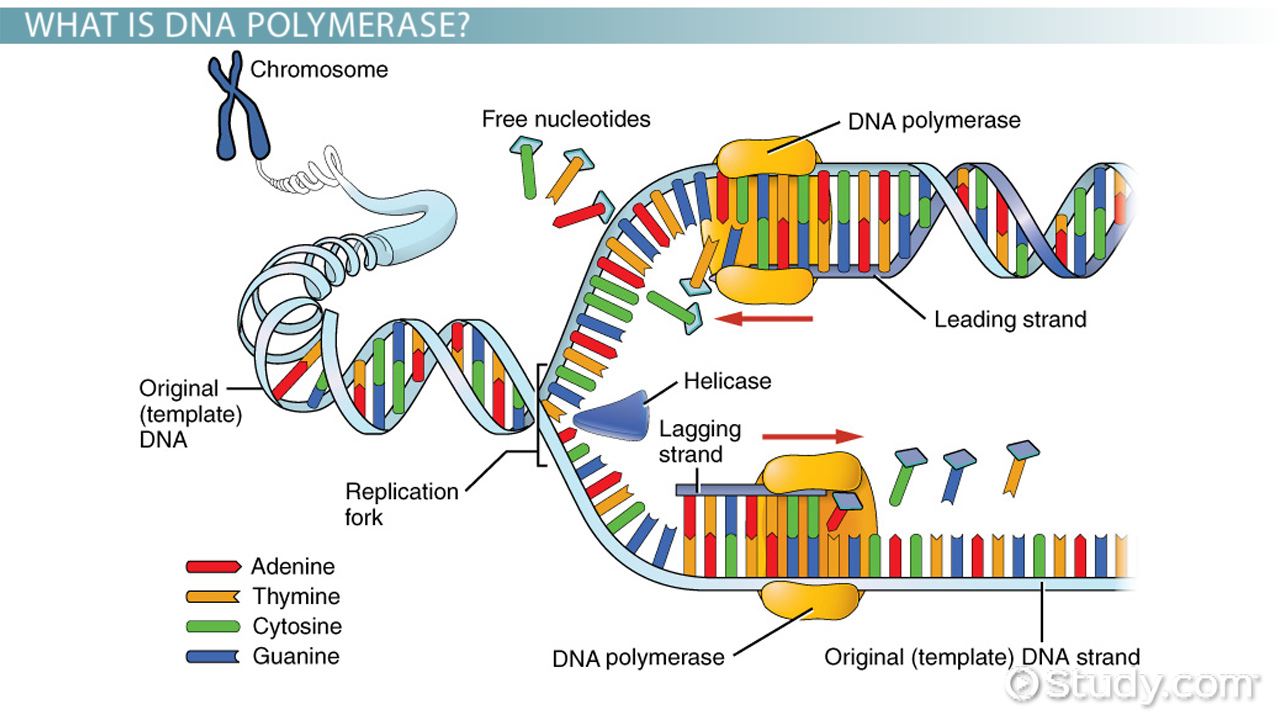
DNA helicase disrupts the hydrogen bonding between base pairs to separate the strands into a Y shape known as the replication fork. This exposed the bases that are typically the rungs of the double helix. The steps involved in the process of DNA replication are as follows.
In DNA replication the genetic information is duplicated to produce two identical copies of the genome of an individual. It is a biological polymerisation which proceeds in the sequence of initiation elongation and termination. In this activity students will recognize that DNA polymerase is responsible for the process of DNA replication during which a double-stranded DNA molecule is copied into two identical DNA molecules.
If you visualize twisting a rope until it twists back on itself you have a pretty good visual of supercoiled DNA. DNA replication occurs during interphase of cell growth. DNA replication is the process by which a molecule of DNA is duplicated.
The DNA copied accurately in the daughter cells. The central enzyme involved is DNA polymerase which catalyzes the joining of deoyribonucleoside 5-triphosphates dNTPs to form the growing DNA chain. List and briefly describe the two basic steps of DNA replication.
The Basic Idea. DNA replication occurs in a series of five steps. This process assures that the daughter cells result.
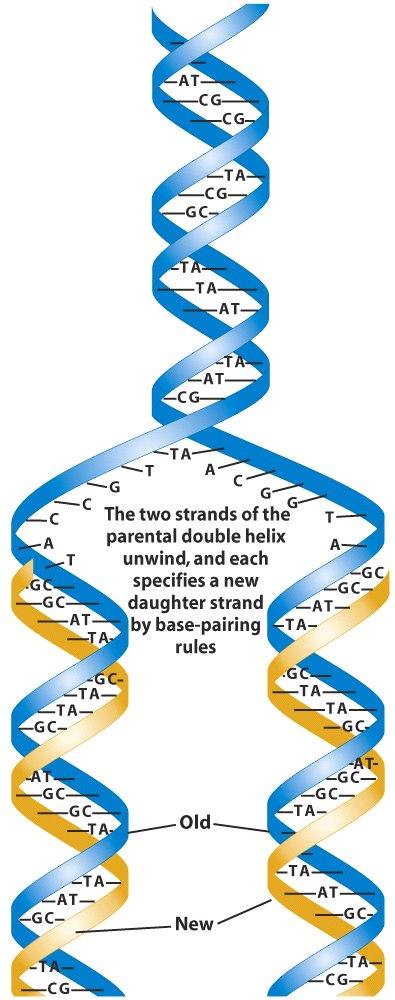
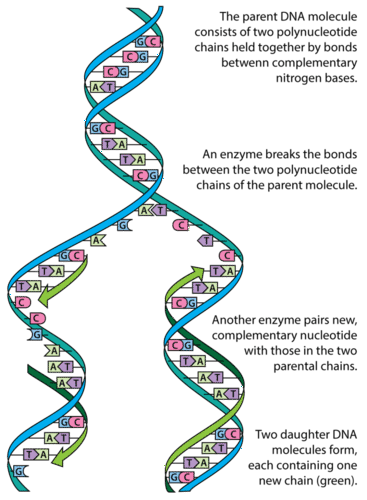
During DNA replication the two parental strands separate and each acts as a template to direct the enzyme catalysed synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand following the normal base pairing rule. DNA replication is a multistep process where new DNA is made. DNA Replication - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf.
DNA replication or DNA synthesis is the process of copying a double-stranded DNA strand prior to cell division in eukaryotes during the S phase of mitosis and meiosisThe two resulting double strands are identical if the replication went well and each of them consists of one original and one newly synthesized strand. When two daughter DNA copies are formed they have the same sequence and are divided equally into the two daughter cells. When cells replicate their DNA they make two identical copies of their DNA from the original copy.
DNA Replication In the process of DNA replication the DNA makes multiple copies of itself. DNA ploymerase catalyze the polymerization of deoxyribonucleotides alongside a DNA strand which they read and use as a template. DNA is directional in both strands signified by a 5 and 3 end.
DNA replication is a fundamental genetic process that is essential for cell growth and division. Helicase opens up the DNA-forming replication forks. DNA replication involve the generation of a new molecule of nucleic acid DNA crucial for life.
These are extended in both directions. Second now that the bases are. DNA unwinds at the origin of replication.
This is performed by an enzyme known as DNA helicase. DNA polymerase III ATP GTP TTP CTP. As discussed in Chapter 3 DNA replication is a semiconservative process in which each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand.
Replicate the DNA of a cell. Replication is the process by which a double-stranded DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical DNA molecules. Three basic steps involved in DNA.
The process of DNA replication can be summarized as follows. First a cell might have a DNA-synthesizing machine which could be programmed to make a particular string of nucleotides for each chromosome. Initiation at the origin of replication unwinding to expose the strands synthesis on both strands with many enzymes adding nucleotides 3 to 5.
First the double helix is unzipped using DNA helicase. For normal growth mitosis occurs. The central enzyme involved is DNA polymerase which catalyzes the joining of deoxyribonucleoside 5-triphosphates dNTPs to form the growing.
DNA replication is the process of producing two identical copies of DNA in which each template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand. DNA replication is important for properly regulating the. DNA replication is a process in which the DNA divides into two same copies during cell division.
The DNA unzips by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs of the two strands. Supercoiled DNA is coiled more tightly than would be typically be found in a cell more than 10 nucleotides per twist of the helix. Energy of Replication The nucleotides arrive as nucleosides DNA bases with PPP P-P-P energy for bonding DNA bases arrive with their own energy source for bonding bonded by enzyme.
It is an enzyme-catalysed reaction. DNA replication is an essential part of cell division as it ensures that each new cell has the same genetic information. Following DNA replication the cell can divide.
DNA replication is one of the most basic processes that occurs within a. During DNA replication each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. Single-strand binding proteins coat the DNA around the replication fork to prevent rewinding of the DNA.
The new strands will be complementary to the parental or old strands. The first step in DNA replication is to unzip the double-helix structure of the DNA molecule. DNA Polymerase is the main enzyme in the replication process.
A second possibility is that the process of replication could break the parental DNA into pieces and use them to seed synthesis of new DNA. DNA replication is a process that all cells must go through prior to any type of cell division. Cells in the body must reproduce to repair damage replace old and nonfunctional cells and promote growth of the body like the liver or bones.
Dna Replication Structure Stages Of Replication Teachmephyiology
What Is The Process Of Dna Replication Example

Molecular Events Of Dna Replication Learn Science At Scitable
Dna Replication Advanced Ck 12 Foundation

Dna Replication Process Youtube

Dna Replication Steps Critical Faqs

Dna Replication Steps Process Mechanism I Research Tweet

Dna Replication Steps Diagram Expii

Dna Replication Steps Process Mechanism I Research Tweet
Topic 2 7 Dna Replication Transcription And Translation Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green

Dna Replication S Phase Checkpoint Control Learn Science At Scitable

Dna Replication The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary

Dna Replication Checkpoint Dna Synthesis Learn Science At Scitable

Dna Replication Structure Stages Of Replication Teachmephyiology

Question Video Identifying The Role Of Dna Ligase In Dna Replication Nagwa

Prokaryotic Dna Replication Enzymes Steps And Significance
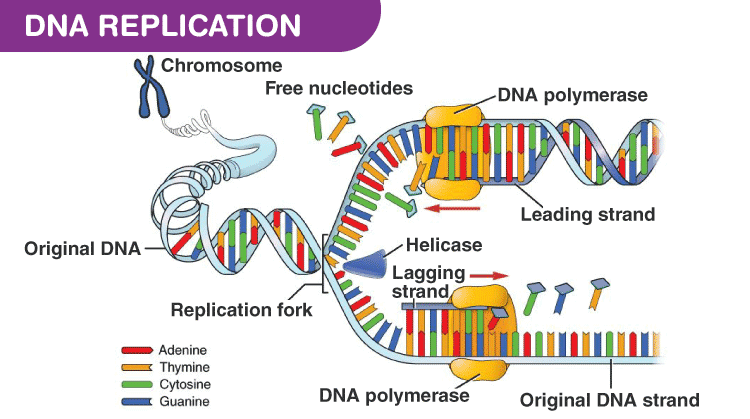
Dna Replication Process With Diagrams Class 12 Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Dna Replication

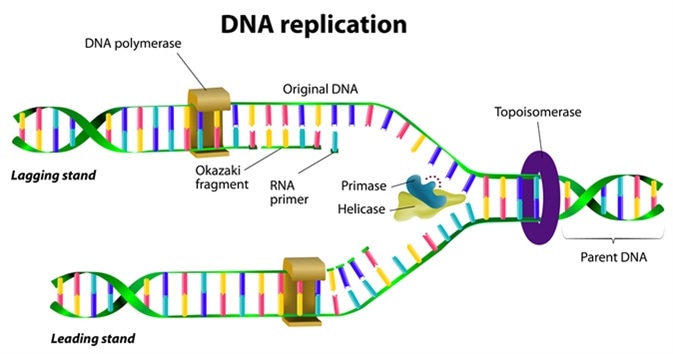
Comments
Post a Comment